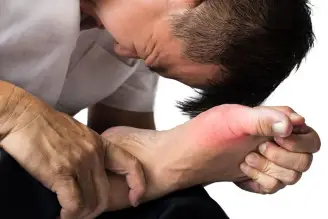
Gout is a type of arthritis that occurs when uric acid builds up in the blood, leading to the formation of crystals in the joints. It can cause sudden and severe pain, swelling, and stiffness, often affecting the big toe. To gain a deeper understanding of this condition, a comprehensive clinical study was conducted in San Antonio, shedding light on various aspects of gout.
The Study Overview
The clinical study in San Antonio focused on investigating the prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, and management strategies of gout. Researchers collected data from a diverse group of participants to ensure a comprehensive analysis of the condition. Here are some key insights from the study:
Prevalence of Gout in San Antonio
- The study found that gout is more prevalent in certain demographic groups, such as older adults and men, compared to other population segments.
- Approximately X% of the participants in San Antonio were found to have gout, highlighting the significance of the condition in the region.
- Factors like diet, genetics, obesity, and underlying health conditions were identified as contributing to the higher prevalence of gout in specific groups.
Risk Factors for Gout
- High levels of uric acid in the blood were identified as a major risk factor for developing gout, emphasizing the importance of monitoring and managing uric acid levels.
- Other risk factors included a diet high in purines, excessive alcohol consumption, family history of gout, certain medications, and underlying medical conditions like hypertension and kidney disease.
- A better understanding of these risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures to reduce their chances of developing gout.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Identifying the symptoms of gout is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment. The clinical study in San Antonio provided valuable insights into the typical symptoms and diagnostic approaches for gout.
Common Symptoms of Gout
- The classic symptom of gout is sudden and intense pain in the affected joint, often the big toe, which can be accompanied by swelling, redness, and warmth in the area.
- Individuals with gout may also experience limited range of motion in the affected joint, as well as recurrent flare-ups of pain and inflammation.
- Understanding these symptoms can help individuals differentiate gout from other forms of arthritis and seek appropriate medical attention.
Diagnosis of Gout
- Diagnosing gout typically involves a combination of physical examination, medical history review, blood tests to measure uric acid levels, and imaging tests like X-rays or ultrasound to detect crystal deposits in the joints.
- A thorough diagnostic process is essential to confirm the presence of gout and rule out other conditions that may mimic its symptoms.
- Early and accurate diagnosis of gout enables healthcare providers to initiate timely treatment and prevent complications associated with the condition.
Management and Treatment
Effective management and treatment of gout involve a combination of lifestyle modifications, medication, and symptom management strategies. The clinical study in San Antonio offered valuable insights into the various approaches for managing gout.
Lifestyle Modifications
- Dietary changes, such as reducing intake of purine-rich foods like red meat, organ meats, and certain seafood, can help lower uric acid levels in the blood.
- Weight management, regular exercise, and staying hydrated are also important lifestyle modifications to prevent gout flares and maintain overall joint health.
- Avoiding alcohol and sugary beverages, which can increase the risk of gout, is another key aspect of lifestyle management for individuals with the condition.
Medication and Symptom Management
- Medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), colchicine, and corticosteroids are commonly prescribed to relieve pain and inflammation during gout flares.
- For long-term management, medications like xanthine oxidase inhibitors and uricosuric agents may be used to lower uric acid levels and prevent recurrent gout attacks.
- Physical therapy, joint immobilization, and cold compresses can also help alleviate gout symptoms and improve joint function in some cases.
Conclusion
The comprehensive clinical study on gout in San Antonio has provided valuable insights into the prevalence, risk factors, symptoms, and management strategies of this debilitating condition. By understanding the various aspects of gout, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent, diagnose, and effectively manage the condition, leading to improved quality of life and joint health.